| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide the Synonyms of This DIG
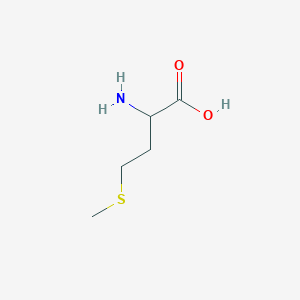
DL-METHIONINE; 59-51-8; methionine; Racemethionine; Acimetion; Banthionine; Cynaron; Lobamine; Meonine; Mertionin; Metione; Urimeth; Dyprin; H-DL-Met-OH; Neston; Pedameth; (+-)-Methionine; DL-2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid; Methionine, DL-; 2-amino-4-(methylsulfanyl)butanoic acid; (+/-)-Methionine; 2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butyric acid; 2-amino-4-(methylthio)butanoic acid; 2-amino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid; Methilonin; alpha-Amino-gamma-methylmercaptobutyric acid; NSC 9241; MFCD00063096; DL-2-Amino-4-(methylthio)-butyric acid; alpha-Amino-gamma-(methylthio)butyric acid; DL-2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butyric acid; CHEBI:16811; (+/-)-2-Amino-4-(methylmercapto)butyric acid; 2-Amino-4-methylthiobutanoic acid; NSC22946; L-Methionine-34S; 2-Amino-4-(methylmercapto)butyric acid; NCGC00159431-02; DL-Methionine, 99+%; DL-Methioninum; .alpha.-Amino-.gamma.-methylmercaptobutyric acid; 26062-47-5; R-Methionine; Methionine, amorphous; D,L-methionine; Methionine DL-; 1006386-95-3; FEMA No. 3301; CCRIS 3717; EINECS 200-432-1; Petameth; Amurex; Metion; Hmet; AI3-18475; NSC-22946; Racemethionine [USAN:USP:NF]; DL-Methionine;; Methionine dl-form; Padameth (TN); alpha-Amino-gamma-methylmercaptobutyric acid (VAN); DL-Met; DL-2-Amino-4-methylthiobutanoic acid; Racemethionine, USAN; 2-amino-4-methylsulfanyl-butanoic acid; dextro,laevo-methionine; DL-Methionine-2-d1; DL-Methionine (JAN); METHIONINE,L-; PubChem20205; Racemethionine (USAN); 2-amino-4-(methylthio)-butyric acid; (.+-.)-Methionine; ACMC-209iba; ACMC-209nhd; DSSTox_CID_821; (.+/-.)-Methionine; Met248; ACMC-1B1LA; DL-Methionine, >=99%; L-Methionine-[1-13C]; SCHEMBL4225; DSSTox_RID_75809; WLN: QVYZ2S1 -L; DSSTox_GSID_20821; 7005-18-7; CHEMBL274119; DL-Methionine (Racemethionine); H3CSCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH; L-Methionine-3,3,4,4-d4; DTXSID9020821; BDBM86195; DL-Methionine-3,3,4,4-d4; FEMA 3301; D-Methionine-d3 (S-methyl-d3); NSC9241; DL-CH3SCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH; DL-Methionine, 99%, FCC, FG; 284665-18-5; CAS_6137; HY-N0325; L-METHIONINE, [METHYL-3H]; NSC-9241; NSC_6137; NSC45689; Tox21_111663; ANW-33287; BBL009323; CAS_84815; DL-Methionine, >=99.0% (NT); NSC-45689; NSC_84815; NSC118113; NSC522406; s9344; STK802463; 2-amino-4-(methylthio) butyric acid; 2-amino-4-methylsulfanyl-butyric acid; AKOS000118924; AKOS016050523; CCG-266195; DB13972; L-Methionine-methyl-[13C,methyl-d3]; MCULE-5626142345; NSC-118113; NSC-522406; CAS-59-51-8; Butyric acid, 2-amino-4-(methylthio)-; NCGC00159431-03; NCGC00159431-04; AK-49717; AK-73057; AK-81252; DS-16180; SY004418; L(-)-Amino-.gamma.-methylthiobutyric acid; DB-029693; (+/-)-2-Amino-4-(methylthio)butyric acid; .gamma.-Methylthio-.alpha.-aminobutyric acid; AM20100433; CS-0008889; FT-0625489; FT-0625547; FT-0671134; FT-0690213; FT-0693483; FT-0698675; FT-0699633; FT-0771524; H2828; M0463; ST50824165; 2336-EP2270005A1; 2336-EP2270008A1; 2336-EP2270011A1; 2336-EP2270018A1; 2336-EP2272834A1; 2336-EP2275404A1; 2336-EP2277867A2; 2336-EP2277898A2; 2336-EP2279741A2; 2336-EP2280003A2; 2336-EP2284157A1; 2336-EP2284178A2; 2336-EP2284179A2; 2336-EP2287165A2; 2336-EP2287166A2; 2336-EP2287167A1; 2336-EP2289892A1; 2336-EP2292088A1; 2336-EP2292615A1; 2336-EP2292617A1; 2336-EP2292620A2; 2336-EP2295055A2; 2336-EP2295410A1; 2336-EP2295550A2; 2336-EP2298761A1; 2336-EP2298780A1; 2336-EP2301929A1; 2336-EP2301935A1; 2336-EP2301938A1; 2336-EP2301939A1; 2336-EP2305219A1; 2336-EP2305674A1; 2336-EP2305689A1; 2336-EP2311453A1; 2336-EP2311823A1; 2336-EP2316470A2; 2336-EP2377842A1; C01733; D04983; DL-Methionine, SAJ special grade, >=99.0%; DL-Methionine, Vetec(TM) reagent grade, 98%; L-.gamma.-Methylthio-.alpha.-aminobutyric acid; Z00115; AB00373904-02; 063M096; Q180341; SR-01000944495; J-300193; L-.alpha.-Amino-.gamma.-methylmercaptobutyric acid; Q-201029; SR-01000944495-1; Z57127440; F0001-1544; C6115881-E914-4EA8-A21A-DCBF67783824; DL-Methionine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Racemethionine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 33807-07-7; 67866-74-4; 67866-75-5; 76408-00-9; 93709-61-6; DL-Methionine, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture, suitable for insect cell culture, >=99%
|
| InChI |
1S/C5H11NO2S/c1-9-3-2-4(6)5(7)8/h4H,2-3,6H2,1H3,(H,7,8)
|
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT