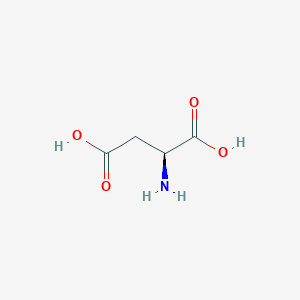
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide the Synonyms of This DIG
L-aspartic acid; aspartic acid; 56-84-8; H-Asp-OH; L-aspartate; Asparagic acid; L-Aminosuccinic acid; (2S)-2-aminobutanedioic acid; aspartate; (S)-2-Aminosuccinic acid; Aspatofort; L-Asparagic acid; Asparaginic acid; L-Asparaginic acid; (S)-Aspartic acid; (2S)-Aspartic acid; (S)-Aminobutanedioic acid; L-Aspartinsaeure; L-Asparaginsaeure; L-Asparaginsyra; Aspartic acid, L-; Acidum asparticum; L-(+)-Aspartic acid; L-Asp; L-2-Aminobutanedioic acid; Aspartate, L-; Asparaginsaeure [German]; Aminosuccinic acid; Butanedioic acid, amino-, (S)-; Aspartic acid (VAN); Asparagic acid (VAN); Asparaginic acid (VAN); Acide aspartique [INN-French]; Acido aspartico [INN-Spanish]; (L)-ASPARTIC ACID; (+)-Aspartic acid; (S)-(+)-Aminosuccinic acid; FEMA No. 3565; CCRIS 6181; Acidum asparticum [INN-Latin]; 25608-40-6; HSDB 1430; L( )-Aminobernsteinsaeure; AI3-04461; NSC 3973; 2-aminosuccinic acid; MFCD00002616; BRN 1723530; Beta-L-Aspartic Acid; L-Aspartic acid-13C4; asp; (S)-(+)-Aspartic acid; (S)-2-aminobutanedioic acid; CHEMBL274323; CHEBI:17053; UNII-Z4FZM6CA61; 39162-75-9; (S)-Aspartate; (+)-Aspartate; 1-Amino-1,2-carboxyethane; (S)-Aminobutanedioate; (2S)-2-azanylbutanedioic acid; L(+)-Aspartic acid, 98+%; Asparaginsaeure; Polysuccinimide; Acido aspartico; Z4FZM6CA61; L-Asparticacid; Acide aspartique; Calcium dihydrogen di-L-aspartate; Polyaspartic acid; 6899-03-2; L-Aspartic acid homopolymer; Calcium diaspartate; Aspartic Acid [USAN:INN]; L-Aspartic acid, homopolymer; (S)-Aminosuccinic Acid; Poly-DL-succinimide; 55443-54-4; 4-04-00-02998 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); EINECS 200-291-6; L(+)-Aminobernsteinsaeure; Aminosuccinate; Asparagate; Asparatate; NSC-3973; l-aspartic-acid; L-Asparagate; L-Aminosuccinate; Aspartic acid [USAN:USP:INN]; (L)-Aspartate; aspartic acid group; alpha-Aminosuccinate; (2S)-Aspartate; Poly-L-asparticacid; EINECS 254-327-0; L-(+)-Aspartate; [3H]-L-aspartate; L-[14C]aspartate; L-Aspartic acid, 2; [3H]L-aspartic acid; (R)-2-aminosuccinate; (S)-2-aminosuccinate; Tocris-0214; [3h]-l-asp; (S)-amino-Butanedioate; alpha-Aminosuccinic acid; (S)-(+)-Aspartate; [3H]-L-aspartic acid; L-Aspartic acid (9CI); 2-Amino-3-methylsuccinate; Biomol-NT_000168; bmse000031; bmse000875; Aspartic acid (USP/INN); EC 200-291-6; L-Aspartic acid (JP17); SCHEMBL3231; (S)-amino-Butanedioic acid; L-Aspartic acid, >=98%; L-Aspartic acid, 99.0%; Lopac0_000133; Aspartic acid, L- (8CI); DL-Aspartic acid, homopolymer; L-Aspartic acid (H-Asp-OH); BPBio1_001128; GTPL3309; GTPL4534; DTXSID7022621; FEMA NO. 3656; aspartic acid (L-aspartic acid); BDBM18125; L-Aspartic acid, >=98%, FG; HMS3260K08; ZINC895032; .alpha.-Aminosuccinic acid, (L)-; HY-N0666; STR04614; Tox21_500133; ANW-32591; PDSP1_000819; PDSP2_000806; AKOS006239578; AKOS015853957; AM81585; CCG-204228; DB00128; LP00133; MCULE-6700641640; SDCCGSBI-0050121.P002; L-Aspartic acid (H-Asp-OH) USP grade; NCGC00024499-01; NCGC00024499-02; NCGC00024499-03; NCGC00024499-04; NCGC00024499-05; NCGC00024499-06; NCGC00024499-10; NCGC00260818-01; 27881-03-4; BP-13291; L-Aspartic acid, Vetec(TM) reagent grade; DB-029944; A0546; CS-0009701; EU-0100133; L-Aspartic acid, BioXtra, >=99% (HPLC); S5632; V1940; L-Aspartic acid, BioUltra, >=99.5% (T); A 9256; C-4546; C00049; D00013; M03000; L-Aspartic acid, SAJ special grade, >=99.0%; A817928; A824434; L-Aspartic acid, reagent grade, >=98% (HPLC); Q178450; SR-01000597734; SR-01000597734-3; F8889-8684; Z1270403519; A4B5FB11-A4B6-4D75-9860-2ACF670700B9; UNII-0O72R8RF8A component CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N; UNII-28XF4669EP component CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N; UNII-30KYC7MIAI component CKLJMWTZIZZHCS-REOHCLBHSA-N; Aspartic acid, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; L-Aspartic acid, certified reference material, TraceCERT(R); Aspartic acid, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; L-Aspartic acid, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture, suitable for insect cell culture; L-Aspartic acid, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; L-Aspartic acid, from non-animal source, meets EP, USP testing specifications, suitable for cell culture, 98.5-101.0%; L-Aspartic acid, PharmaGrade, Ajinomoto, EP, JP, USP, manufactured under appropriate GMP controls for Pharma or Biopharmaceutical production, suitable for cell culture
|
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT
 click to show the detail info of this DBT
click to show the detail info of this DBT